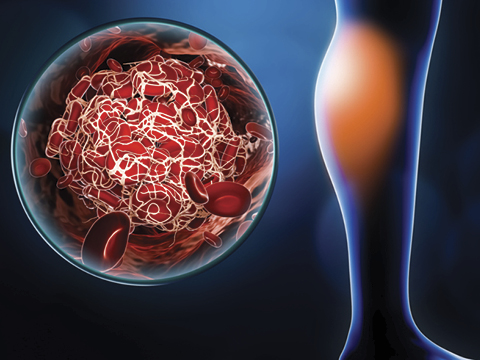
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition in which a blood clot develops in the deep veins, typically in the leg or lower extremities. It occurs when blood flow in the veins slows down or becomes impaired, leading to accumulation of blood and the formation of a blood clot. DVT can cause pain, swelling, and tenderness in the affected leg, and if left untreated, the blood clot can break loose and travel to the lungs, causing a potentially life-threatening condition called pulmonary embolism. Treatment options for DVT may include blood thinners, compression stockings, and, in some cases, surgical intervention.
Chronic Atrial Fibrillation
Chronic atrial fibrillation is a common type of heart rhythm disorder that involves irregular and rapid beating of the heart’s upper chambers, called the atria. Chronic atrial fibrillation is characterized by episodes that typically last more than seven days and may require medical treatment to revert the heart to normal rhythm. This condition can result in various symptoms, including palpitations, shortness of breath, fatigue, and dizziness, and it increases the risk of complications such as stroke and heart failure.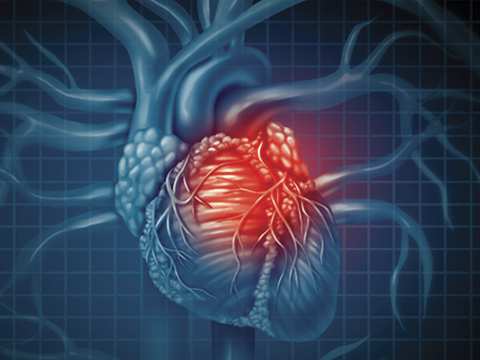
Mechanical Heart Valve
Mechanical heart valve refers to a condition where an individual has a mechanical valve implanted in their heart. This condition may arise due to various reasons, such as congenital heart defects, heart valve disease, or valve replacement surgery. Mechanical heart valves are artificial devices designed to replace damaged or diseased heart valves. They are typically made of durable materials like metal or carbon-based materials and are crafted in a way that mimics the function of a natural valve. While mechanical heart valves may be effective in improving blood flow and ensuring proper circulation, they also require regular monitoring and the use of blood thinner medications to prevent blood clots from forming around the valve.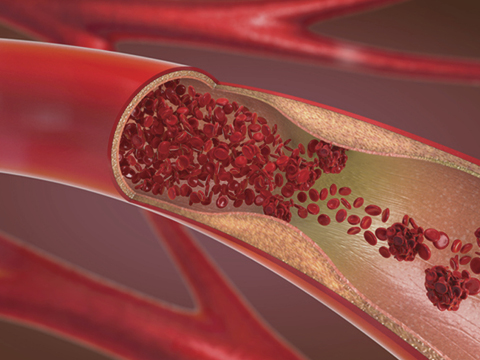
Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism refers to a medical condition where a blood clot develops in one of the arteries located in the lungs, usually due to a clot in the leg. The blood clot obstructs the blood flow to a section of the lungs, leading to possible damage to the lung tissues and causing various symptoms such as sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, coughing up blood, rapid heart rate, and fainting. If left untreated, pulmonary embolism can be life-threatening. Treatment typically involves the use of blood thinners to dissolve the clot or surgical interventions in severe cases.
Venous Thromboembolism
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a condition characterized by the formation of blood clots that blocks blood flow in the veins.
- “Venous” means in the veins
- “Thrombo” means a blood clot
- “Embolism” means a circulation particle that causes an obstruction
This disorder can lead to two different kinds of blood clotting conditions: deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
